Other vision loss
- Comorbidity correction (COMO)
- Crosswalk data points that span multiple vision loss categories
- DisMod-MR 2.1
- Split into moderate and severe vision loss
- Squeeze into severity-specific vision loss envelope
Otitis media
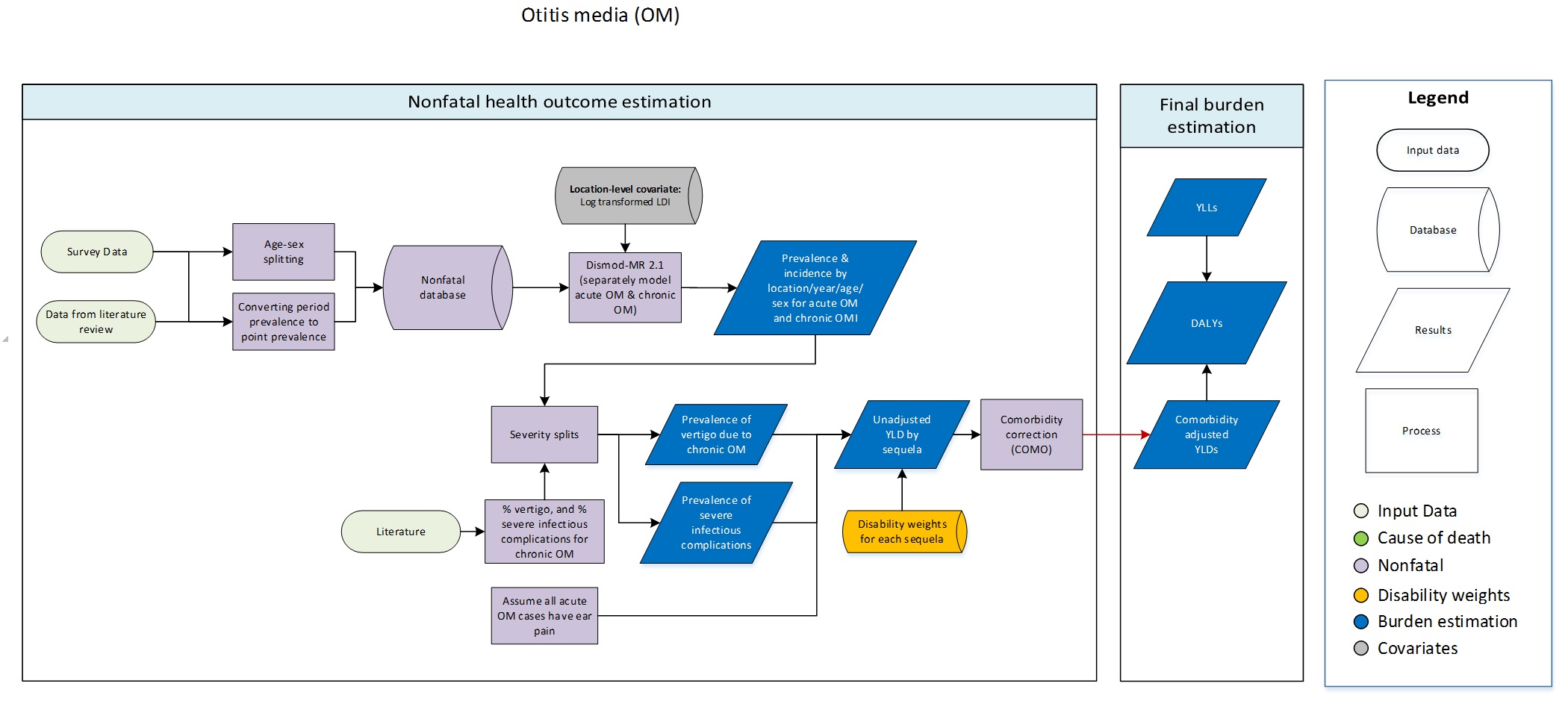
- Severity split (% vertigo and % severe)
- Age sex splitting
- Assume all acute cases have ear pain
- Comorbidity correction (COMO)
- Converting period to point prevalence
- DisMod-MR 2.1
- Severity splits
Outpatient
- Format and standardize ICD codes
- Map and aggregate to modeling causes
- Aggregate individual injury causes to make grouped injury causes
- Calculate prevalence and inciden correction factors
- Apply appropriate Marketscan correction factors to hospital data
- Apply age/sex restrictions
Pancreatitis
- Adjustment from primary code to all code based on Claims data
- Comorbidity correction (COMO)
- Computing excess mortality from available incidence & CSMR data
- Meta-analysis of % mild/mod/severe pancreatitis
- Severity splits
- DisMod-MR 2.1
Paralytic ileus and intestinal obstruction
- Adjustment from primary code to all code based on Claims data
- Comorbidity correction (COMO)
- Computing excess mortality from available incidence & CSMR data
- DisMod-MR 2.1
Parkinson Disease
- Age-sex splitting and Age-splitting
- CODEm
- Comorbidity correction (COMO)
- Dismod-MR 2.1 (model 1)
- Dismod-MR 2.1 (model 2)
- EMR regression using countries with highest CSMR to prevalence ratios
- Select countries with the highest CSMR/ prevalence ratios
- Garbage code redistribution
- ICD mapping
- Meta-analysis of % mild, moderate, severe Dementia
- Noise reduction
- Severity splits
- Standardize input data
Pelvic Inflammatory Disease
- etiology attribution
- Comorbidity correction (COMO)
- Dismod-MR 2.1
- Severity splits
- Squeeze to sum to 1
Peptic Ulcer Disease
- Causal attribution of anemia sequelae
- Adjustment from primary code to all code based on Claims data
- Comorbidity correction (COMO)
- Computing excess mortality from available incidence & CSMR data
- DisMod-MR 2.1
- Age-sex splitting
- Subtract prevalence of symptomatic episodes from prevalence of chronic PUD
- Severity splits of symptomatic PUD
- Meta-analysis of % mild and mod PUD
Periodontal diseases

- Comorbidity correction (COMO)
- Correction for proportion of the population with edentulism
- Dismod-MR 2.1
Peripheral Arterial Disease

- Age sex splitting
- Comorbidity correction (COMO)
- Disability weights for each sequela
- DisMod-MR 2.1
- Split overall prevalence by proportion
Permanent caries

- Calculation of D/DMF ratio for all data where both measures exist, for ages
- Calculation of incidence as the DMF increment between adjacent ages for ages
- Comorbidity correction (COMO)
- Conversion of DMF scores to dental caries prevalence using d/dmf ratio calculated from the same row, study, or location
- Correction for proportion of the population with edentulism
- Dismod-MR 2.1; excess mortality rate set to 0
- Meta-analysis of percent of conditions associated with edentulism and severe tooth loss
- Severity splits
Pneumoconiosis
- Geographic exclusions
- Meta-analysis of mild, moderate, severe
- Severity splits
- Comorbidity correction (COMO)
- Computing excess mortality
- DisMod-MR 2.1
Polycystic ovarian syndrome

- Adjustment from primary code to all code based on Claims data
- Comorbidity correction (COMO)
- Dismod-MR 2.1
- Meta-analysis of % mild, moderate, severe PCOS
- Severity splits
Premenstrual syndrome

- Adjustment from primary code to all code based on Claims data
- Comorbidity correction (COMO)
- Pregnancy adjustment
- Dismod-MR 2.1
Protein-energy malnutrition

- Proportion of children with edema & weight-for-height z-score < -2SD, < -3SD by geography-year
- DisMod-MR 2.1 Single parameter proportion model
- Multiply prevalence of WHZ < -3SD by proportion of WHZ < -3SD with edema by geography-age-sex-year
- Zero out prevalence for population over five years old
- Subtract from the prevalence of WHZ < -3SD the proportion of WHZ < -3SD with edema by geography-age-sex-year
- Subtract proportion of edema among WHZ < -3SD from proportion of WHZ < -2SD with edema by geography-age-sex-year
- Multiply prevalence of WHZ < -2 SD to < -3 SD by proportion of WHZ < -2 SD to < -3SD with edema by geography-age-sex-year
- Calculate weight-for-height (WHZ) z-score using WHO Child Growth Standards (2006)
- Collapse into geography-year-age-sex proportion of WHZ < -2SD, WHZ < -3SD
- ST-GPR linear mixed effects model
- Subtract prevalence of WHZ < -3SD from prevalence of WHZ < -2SD by geography-age-sex-year
- Subtract proportion of moderate wasting with edema from moderate wasting by geography-age-sex-year
- Proportion of children under five with WHZ < -2SD, WHZ < -3SD
- DisMod-MR 2.1 Single parameter proportion model (WHZ < -2SD, WHZ < -3SD); Full parameter model (including prevalence and incidence) (WHZ < -2SD)
- Calculate prevalence to incidence ratio for each geography-year-age-sex
- Scale prevalence to equal prevalence from full parameter model for > 5 years (< 5 years remains the same)
- Apply ratio to prevalence to calculate incidence
- Calculate wasting counterfactual after cure of heavy infestation of ascariasis, trichuriasis, and hookworm
- Subtract severe wasting due to helminths from severe wasting without edema
- Comorbidity correction (COMO)


